Before talking about the types and used areas of flow meters, in industry, it is necessary to define Fluid and Flow.
Fluid:
A fluid is a substance that changes shape significantly and continuously under the influence of a very small force, that is, it can easily flow and takes the shape of the container in which it is placed.
Definitions Related to Fluids
Fluid Types: Solid (granular), Liquid, Gas, and multiphase fluid
Perfect Fluid: Zero viscosity (frictionless flow), incompressible
Real Fluid: non-zero viscosity and compressible
Viscosity: Resistance of the fluid to flow
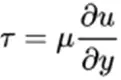 μ, viscosity constant, velocity gradient (∂u/∂y)
μ, viscosity constant, velocity gradient (∂u/∂y)


Flow measurement flow profile is laminar flow velocity: 1-2 m/sn,
Pipe locations with Reynolds number < 2100 should be preferred.
Flow rate:
If the total resultant force acting on the solid, liquid and gas fluids in a volume is different from zero, the fluid starts to move in the direction of the force and gains a speed proportional to its acceleration. Flow rate is equal to the multiplying of this speed value and the cross-sectional area of the volume it fills, that is;
Q:Flow rate m3/s
V:Speed m/s
A:Cross-sectional area m2
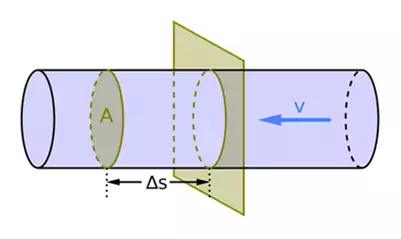
Q=V*A, m3/s volumetric flow rate
D: Fluid density: g/cm3, If it is taken as Ton/m3
Q= (V*A)*D= Ton/sn*3600=Ton/h
As a result, the flow rate units for liquids and gases can be derived as m3/h, m3/sn, l/h, I/min, l/sn in volumetric units, Sm3/h, Sl/h, Nm3/h, Nl/h for gases or Ton/h, Kg/h, g/sn… in mass units.
Gas or liquid meters and flowmeters are indispensable devices of industry and daily life. These devices used to measure the total amount or flow rate of the fluid are the most practical, economical and healthy solution for this process.
Meters and flow meters, which are used in petroleum, chemical, water, natural gas, wastewater, food, paint, cosmetics, automotive, construction, textile and all other industrial facilities where fluids are used, prevent time, labor and cost loss, as well as contribute to accurate cost calculation and improvement of production quality.
In facilities and quality control laboratories where water, wastewater, fuel, natural gas, solvents, acids, oils, liquid foods and other liquids and gases are used, it is essential to measure the fluid flow rate to ensure complete control.
The appropriate flow meter must be selected depending on the area of use and process conditions.
Flowmeters are used in all types of industries; Chemical-Petrochemical, Fuel-Gas, Energy, Paper, Food-Beverage, Water and Wastewater Treatment, Mining processes and inventory applications.
Flowmeter types are generally called:
Those that measure in volumetric or mass units in fully filled pipelines
Those that measure in volumetric units in partially filled pipelines
or Open channel flowmeters.
Some Types of Flowmeters Used in Different Industries:
- Vorteks/Swril flowmeter (Clean liquids, gases, steam; Mass/volume units)
- Thermal Mass flowmeter (Gases; Mass/volume units)
- Electromagnetic flowmeter (Electrical conductivity>5microS/cm liquids; Volumetric units)
- Transit Time Ultrasonic flowmeter (Clean Liquids 10-20Bppm; Volumetric)
- Doppler flowmeter (All dirty or clean liquids containing min. 75ppm solids; Volumetric units )
- Coriolis flowmeter (Gas or liquid clean fluids; Mass/Volumetric units)
- Turbine flowmeter (Gas or liquid clean fluids; Volumetric units)
- DP Differential Pressure flowmeters (Gas, liquid clean; Mass/Volumetric units)
- (PD) Positive Displacement flowmeters (Liquid viscous fluids; Mass/Volumetric units)
- Rotameter/Variable Area flowmeter (Liquid and gaseous fluids; Volumetric units)


